Classification of Engines:
Engine cycle
- Otto cycle Engine
- Diesel cycle Engine
Number of Strokes
- Two stroke
- Four stroke
Fuel used
- Petrol Engine
- Diesel Engine
Types of Ignition
- Spark ignition
- Compression Ignition
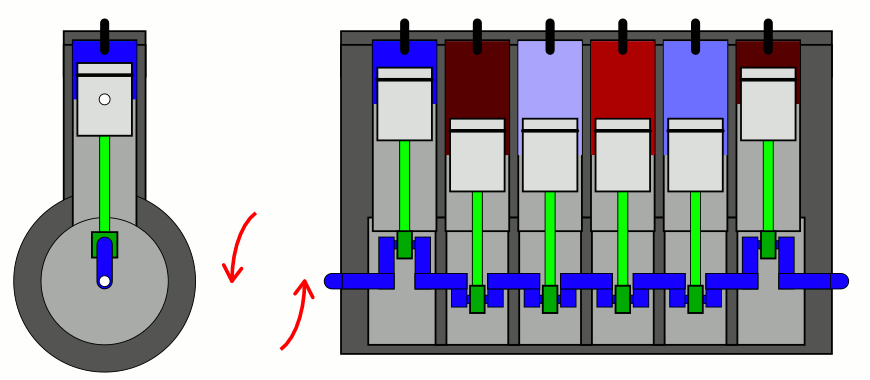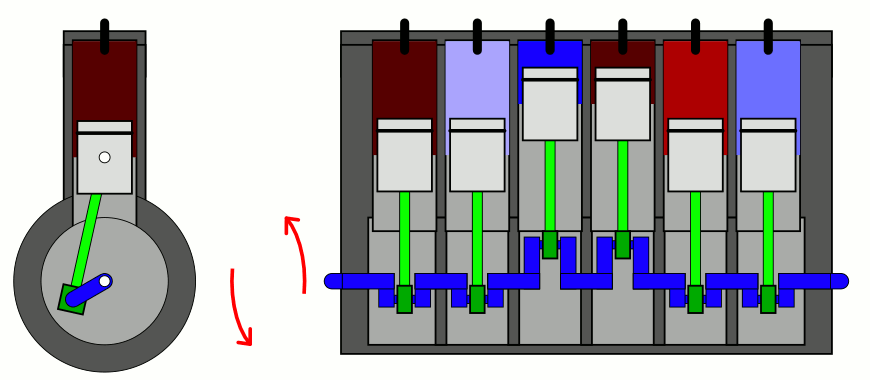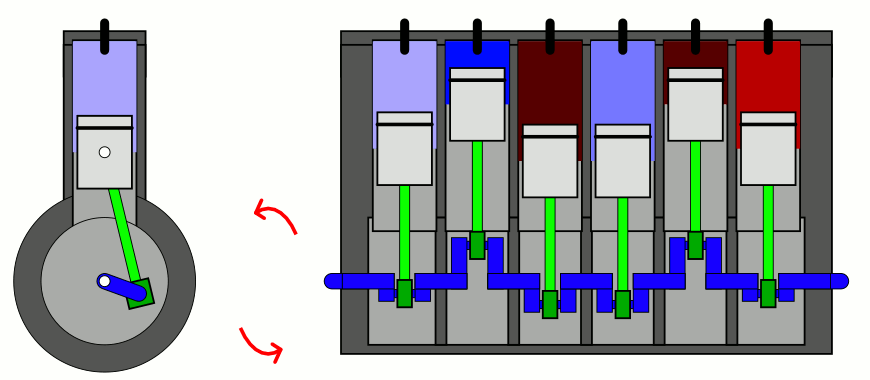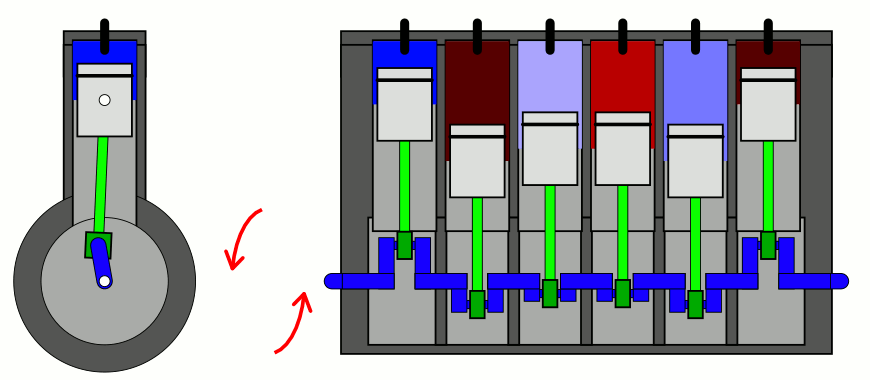
Number of arrangement of Cylinders
- Single Cylinder Engines
- Two Cylinder Engines
- In-Line Vertical type
- V-type
- Opposed type
- Three cylinder Engines
- Four Cylinder Engines
- In-line Vertical type
- V-Type
- Opposed type
- Six and Eight cylinder Engines
- Radial Engines
Square Engine:
An engine having Stroke equal to Bore. If Stroke / Bore ratio is more than 1, it called “under-square”, while if it is less than 1, it is called “over-square”.
Boxer Engine:
Horizontally opposed engine, where opposing pistons are attached to different crank pins
Wankel Engine:
Engine working on Otto cycle, but the piston having rotary motion. Notable cars which used are Mazda RX-7 and Mazda R-8. Advantages are compact, simpler construction due to far less number of working parts compared to conventional engines, very smooth running, balancing is easier, higher volumetric efficiency, lesser wear of the rotor and better reliability due to lessor speeds of the rotor, low NOx emissions and lower octane fuel can be used. Disadvantages are less torque produced at lower speeds, lower thermal efficiency resulting in higher fuel consumption and higher production cost due to smaller quantity.
 Atkinson cycle Engine:
Atkinson cycle Engine:
Engine developed by James Atkinson, working on modified Otto cycle, called Atkinson cycle, wherein the compression stroke is shorter than the expansion stroke. Used in “Toyota Prius”.
Miller cycle Engine:
Atkinson cycle engine with a supercharger. An example is the “Mazda Eunos 800 M” Engine
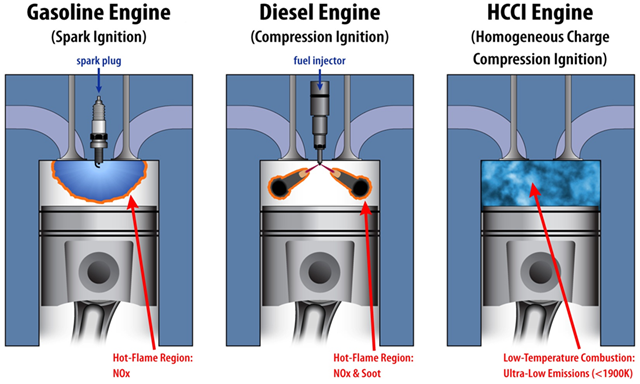
HCCI Engine:
An IC engine in which well mixed fuel and air mixture is compressed to the point of auto-ignition. It has the characteristics of both S.I as well as C.I. engines. Advantages are, higher efficiency and lower emissions compared to conventional engines. Disadvantages are high peak pressures and heat release rates, difficulty to control and higher pre-catalyst emissions of HC and CO, due to which it has not been used so far in any production vehicle.
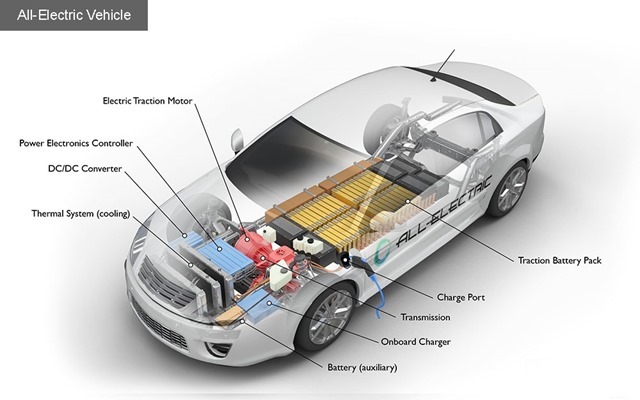
Electric Vehicle:
Advantages are quick acceleration, noise free operation, no emission, high reliability, easy maintenance, regenerative braking, no loss of power in idling and easy to drive. Disadvantage are limited range, low top speed, limited life of batteries, and substantial cost of replacement of batteries.
Hybrid Systems:
Main components are Heat engine, Fuel tank, Electric Motor, Generator, Batteries and Transmission systems. Types of systems are Series type, Parallel type and Series-Parallel types. Recent examples are Honda "Insight” and Toyota “Prius”. Battery for these should be able to provide high power in short pulses from 1 – 1.5 KWh. I.e. should be able to provide many shallow charging cycles.
Plug-In Hybrid (PHEV):
A hybrid vehicle with batteries which can be recharged from ordinary household electric plug. At present, PHEVs are not yet in production. Operating modes of PHEV are Charge-depleting mode, Charge-sustaining mode, Blended mode and Mixed mode. These need a large battery to provide energy in charge-depleting mode for a defined distance, say 10 KWh for 64 kms or 5 KWh for 16 kms range.
Fuel Cell:
A power source for the future automobiles. Fuel cells produce electricity through chemical reaction with no harmful exhaust emissions. Recent examples are GMs “Hy-Wire” and “Sequel” and Honda’s “FCX”.