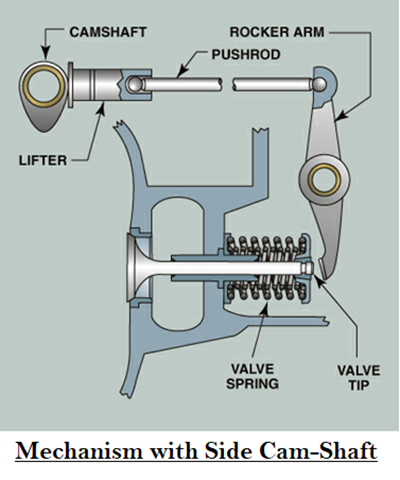
Valve Actuating Mechanisms:
Each valve must open at the proper time, stay open for the required length of time and close at the proper time. Hence the timing of the valves are controlled by valve actuating mechanisms. Intake valves are just open before the piston reaches the Top Dead Centre (TDC), and exhaust valve remain open after TDC. At this particular instant both valves are open at the same time. This overlap results in better volumetric efficiency and lower operating temperatures.- Mechanisms with side camshaft
- Double row side valve (T-Head) type
- Single row side valve (L-Head) type
- Overhead inlet and side exhaust valve (F-Head) type
- Single row overhead valve (I-Head) type
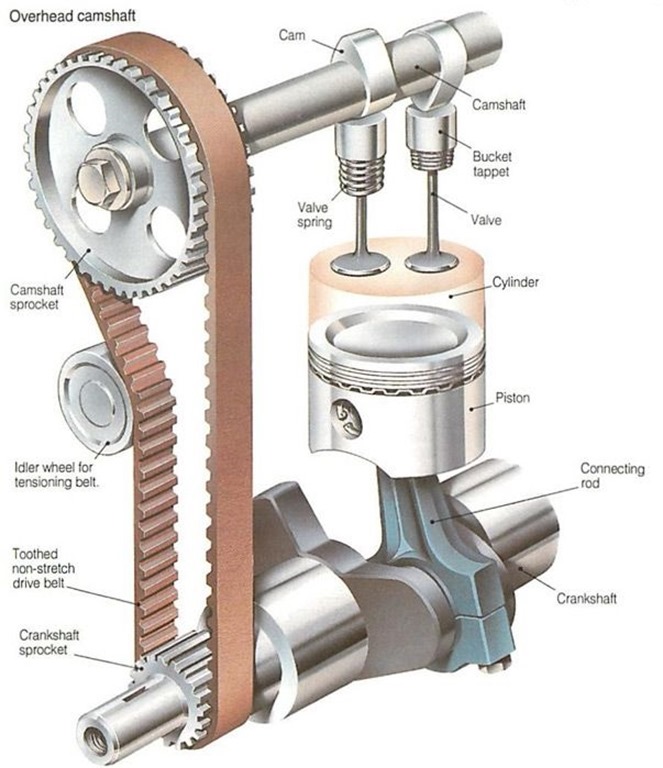
- Mechanisms with overhead camshaft
- With inverted bucket type follower operated by single camshaft
- With end-pivoted rocker arm operated by single camshaft
- Inlet valve operated by inverted bucket type follower and exhaust valve by pivoted rocker arm (Double camshaft)
- Double overhead camshaft with inverted bucket type followers
- Double overhead camshaft with separate rocker arms
Valve Train Components:
- Camshaft
- Camshaft drive
- Chain drive
- Gear drive
- Toothed belt
- Valve tappet
- Solid Lifters
- Roller lifters
- Hydraulic lifters
- Followers
- Push rod
- Rocker arm and rocker shaft
Camshaft:
A Shaft with a cam for each intake and exhaust valve. Each cam has a high spot called cam-lobe which controls the valve opening. Camshaft actually controls rotary motion to reciprocating motion.
Camshaft drive:
Cam gear is twice as large as crank gear. This makes the cam turn at 1/2 the speed of the crank
Valve Tappets:
The tappet follows the cam lobe and pushes the push rod. Solid and Roller lifts require adjustable rocker arm. Hydraulic Tappet requires oil to control.
Push Rods:
Metal rod which transfers force from the lifter to the rocker arm
Rocker Arm:
Rocker arm transmit the forces of the pushrod to the valve
Variable Valve Timing (VVT) technologies:
VVT is an engine technology which allows the lift or duration or timing (some or all) of the intake or exhaust valves to be changed during the engine operation
- Phase changing systems
- Profile switching systems
- Variable event timing systems
- Variable lift systems
- Electronic valve actuating systems
VVTi Engines:
VVTi system is a cam phasing system that can be applied on both inlet and exhaust cam shafts. This movement is controlled by engine management system according to need and actuated by hydraulic valve gears.
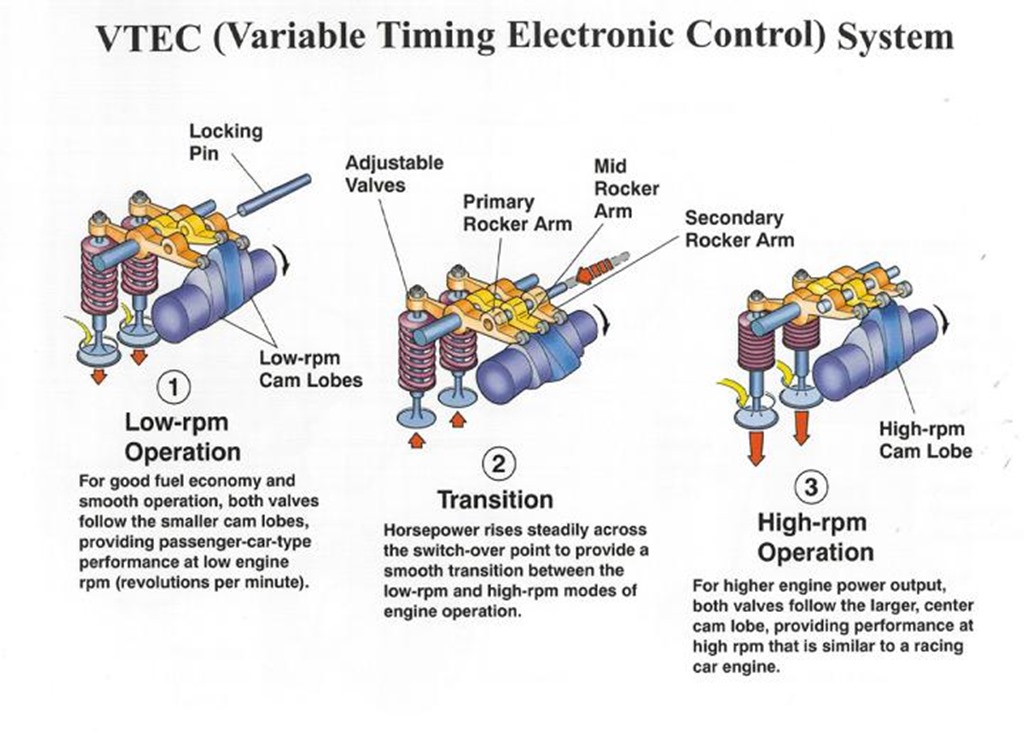
VTEC Engines:
VTEC stands for Valve Timing Electronic Control, where the system set the optimum valve timing by continuous changing of timing to open or close in Intake and Exhaust valves in response to the engine load, rotation and other operating conditions. This system controls the emission of NOx and HC and the fuel economy is increased.
i-VTEC:
iVTEC stands for Intelligent VTEC. Honda implement this most successful valve actuation system by continuously variable intake valve timing and computer controlled management for optimized torque output and fuel efficiency.
AVTEC:
AVTEC stands for Advanced VTEC. Honda implement this continuously variable phase control system to respond to the drivers power needs independent of engine speed. This system presents 13% better fuel economy and 75% lower emissions than iVTEC.
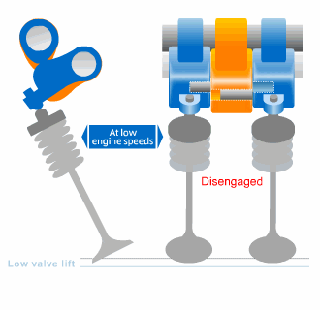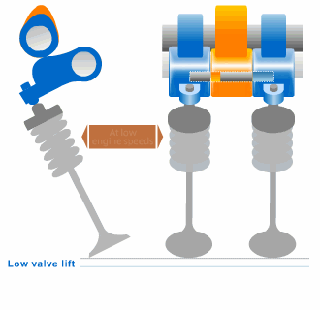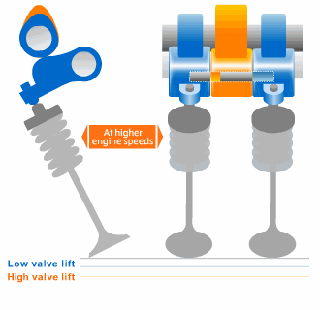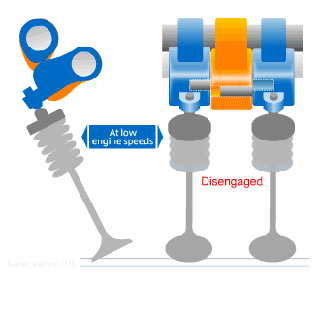
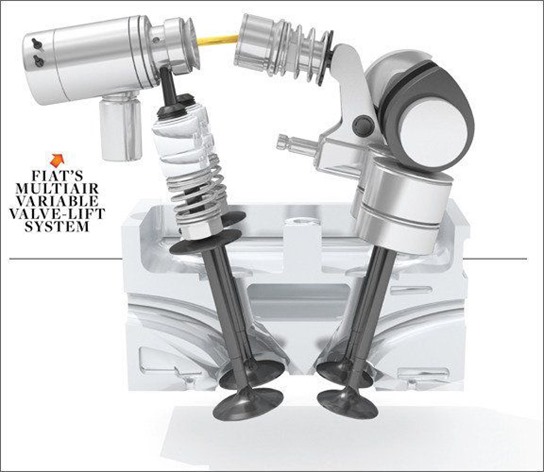
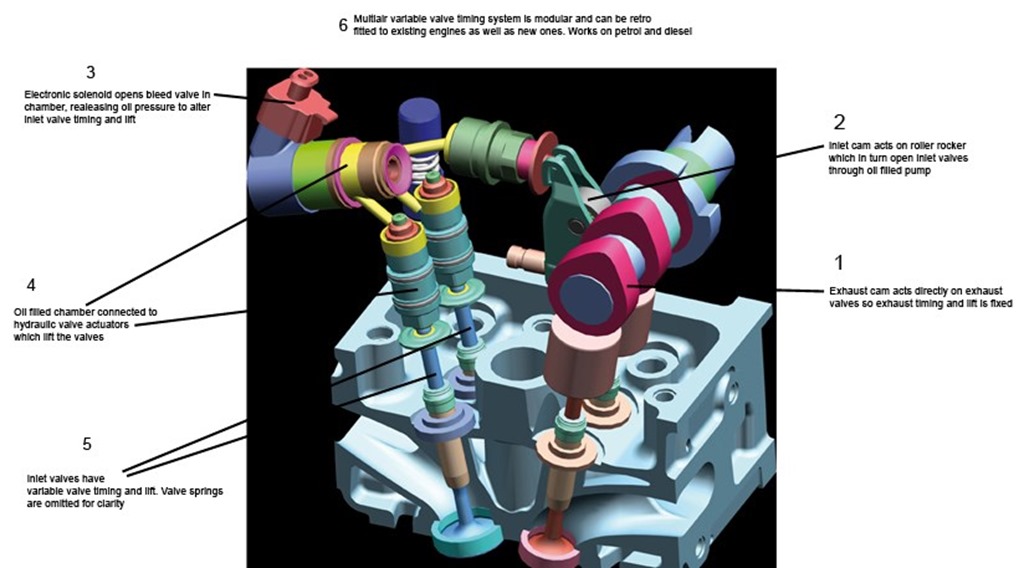
FIAT Multi - Air Technology:
A new engine air management technology introduced by FIAT which is much better than any VVT technology
Valve Troubles:
- Burning of valve face
- Necking of valve stem
- Valve face wear
- Valve stem and guide wear
- Valve cracking or Breakage
- Noisy valve operation










No comments:
Post a Comment