Main Engine Parts:
- Cylinder Block and Crank case
- Cylinder Head
- Sump or Oil Pan
- Manifolds – Inlet and Exhaust
- Gaskets
- Cylinders and Liners (Dry and Wet)
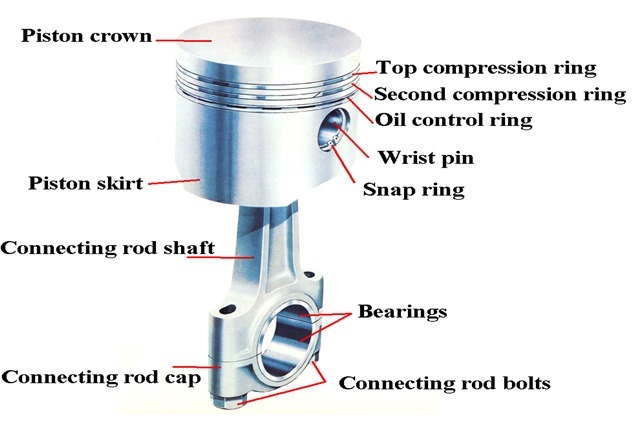
- Pistons
- Piston Rings
- Connecting Rods
- Piston pins
- Crankshaft
- Main Bearings
- Valves and Valve – actuating mechanisms
- Catalytic converter, Muffler and Tail pipe
Functions of Piston:
- To transmit the force of explosion to the crankshaft
- To form a seal so that high pressure gases in the combustion chamber do not leak into the crankcase
- To serve as a guide and a bearing for small end of the connecting rod.
Piston Requirements:
- Should be silent in operation both during warming up and the normal running
- Design should be such that the seizure does not occur
- Should offer sufficient resistance to corrosion
- Shortest possible length
- Light in weight
- High thermal conductivity
- Long life
Methods to avoid Piston Slap:
- Use of Horizontal / Inclined slots
- Use of vertical or T-Slots
- Taper pistons
- Oval pistons
- Use of Special alloys
- Wire-wound pistons
- Autothermic pistons
- Bi-metal pistons
- Offset piston
Special Pistons:
- Pistons with inserted ring carrier
- Cast steel pistons
- Anodized pistons
- Tinned Pistons
- Oil-Cooled pistons
- Two-piece Pistons
- Composite insulated (heat shielded) pistons
- Squeeze cast pistons
- Aeconoguide pistons
Types of Piston Failure:
- Piston scuffing
- Burnt piston
- Damage to ring land
- Damaged piston boss and circlip groove
Functions of Piston rings:
- To form a seal for the high pressure gases from the combustion chamber against leak into the crankcase
- To provide easy passage for heat flow from the piston crown to the cylinder walls
- To maintain sufficient lubricating oil on cylinder walls throughout the entire length of piston travel
Types of Rings:
- Compression Rings
- Plain
- Taper face
- Torsional wrist
- Scraper type torsional twist
- Taper face torsional twist
- Keystone type
- Oil control Rings:
- Bevelled
- Stepped Scraper
- Slotted scraper
- Delayed action scraper
- Double action scraper
- Composite rail scraper
Cause of Ring Failure:
- Rapid Wear
- Scuffing
- Ring Breakage
Connecting Rod:
It’s function is to convert the reciprocating motion of the piston into rotary motion of the crankshaft
Piston Pin:
It connects the piston and the connecting rod. It also called as “Gudgeon pin”.
Crankshaft:
It is the engine component from which power is taken
Crankshaft assembly:
Includes the crankshaft and Bearings, flywheel, vibration damper, sprocket or gear to drive camshaft and oil seals at front and rear
Main parts of Crankshaft:
- Main Journals
- Crank Pins
- Crank Webs
- Counter Weights
- Oil Holes
Technorati Tags: What are the main parts of an engine,How many parts are there in engine,car engine parts and function diagram,all the piston parts explained,how does the piston work,what is the function of the piston in an engine,what is the function of piston rings,what does the camshaft do,piston function requirements and types

















No comments:
Post a Comment